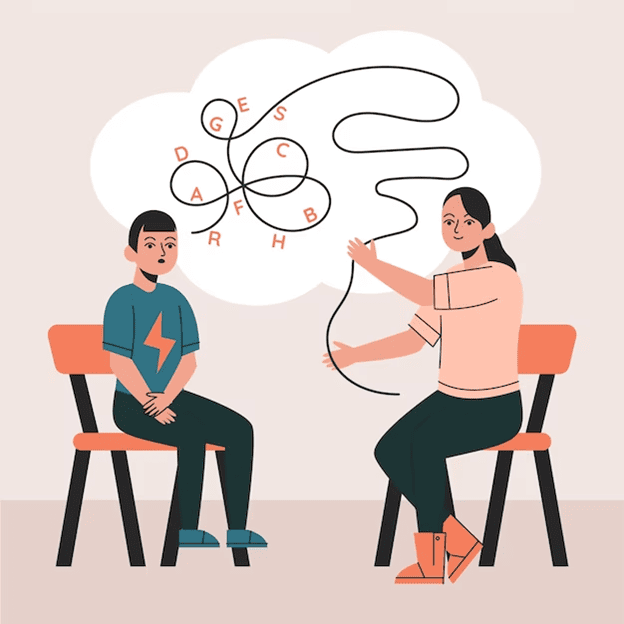
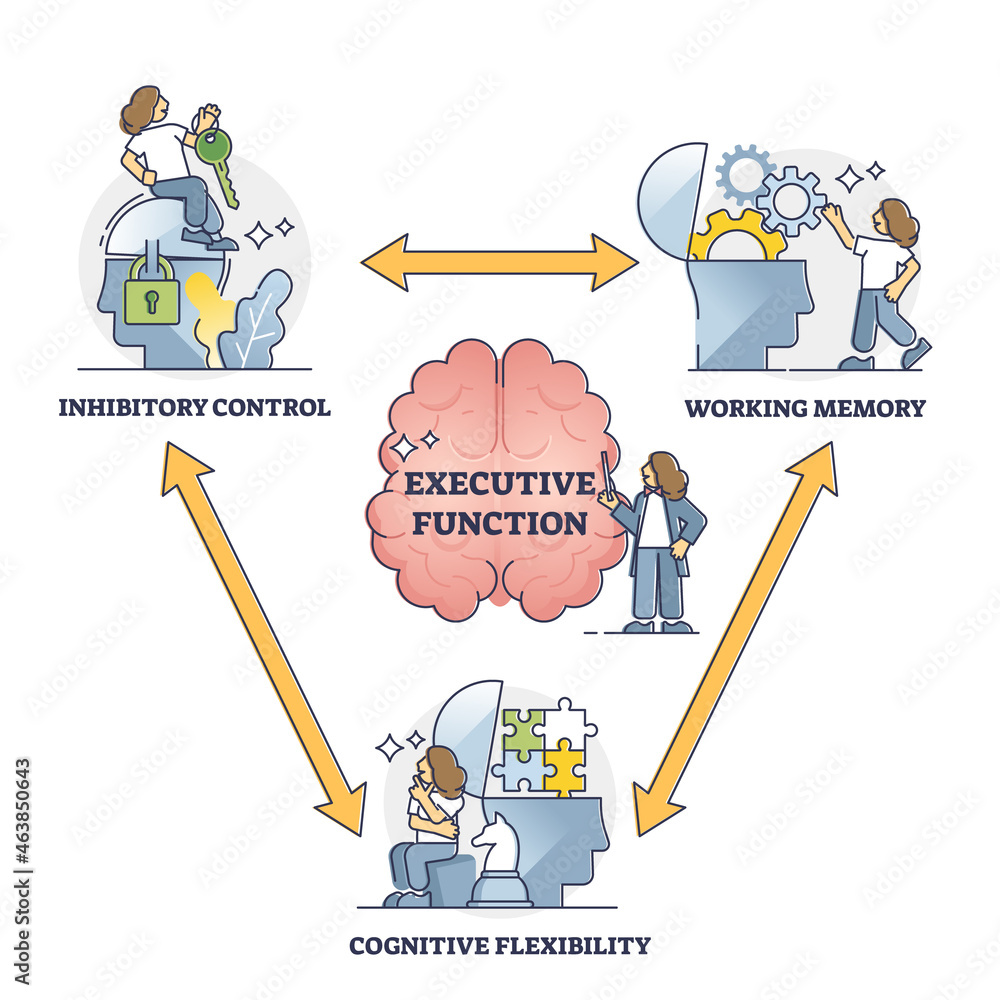
Cognitive Inhibition
Cognitive Inhibition - Inhibition is a key concept in psychology because so much of successful behavior depends on it: This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. We need to inhibit distracting information in order. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task.
Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. Inhibition is a key concept in psychology because so much of successful behavior depends on it: This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. We need to inhibit distracting information in order.
Inhibition is a key concept in psychology because so much of successful behavior depends on it: This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. We need to inhibit distracting information in order. Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of.
Executive function or cognitive control, vector illustration outline
Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. We need to inhibit distracting information in order. This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod,.
Comprendre l'inhibition définition et explications
Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. Inhibition is a key concept.
Brain activation differences among four age groups for tasks tapping
We need to inhibit distracting information in order. Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Inhibition is.
Unconscious inhibition separates two forms of cognitive control PNAS
This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Inhibition is a key concept in psychology because so much of successful behavior depends on it: Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. We need to inhibit distracting information in order. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping.
What is Memory Inhibition? [Definition and Example] Understanding
Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. We.
Common and distinct activation regions between two (A
Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Inhibition.
What is INHIBITION? definition of INHIBITION (Psychology Dictionary)
Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. Inhibition.
Cognitive Inhibition and Emotion Regulation in Depression Jutta
Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. We need to inhibit distracting information in order. This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Cognitive inhibition,.
Figure 1 from Cognitive Inhibition Modifies the Affective and Incentive
Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. We need to inhibit distracting.
L'inhibition cérébrale dans l'apprentissage des sciences
Inhibition is a key concept in psychology because so much of successful behavior depends on it: Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task. Cognitive inhibition, ‘the stopping or overriding of a mental process, in whole or in part, with or without intention’ (macleod, 2007), requires mediating. This chapter illustrates.
We Need To Inhibit Distracting Information In Order.
This chapter illustrates the development of cognitive inhibition using theories, definitions, and research evidence. Inhibition is a key concept in psychology because so much of successful behavior depends on it: Reviews evidence suggesting that inhibitory processes become more efficient between early childhood and adulthood / highlights some of. Cognitive inhibition refers to the active suppression of irrelevant cognitive information or processes in working memory, enhancing task.



![What is Memory Inhibition? [Definition and Example] Understanding](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/YLySgGlSRck/maxresdefault.jpg)




