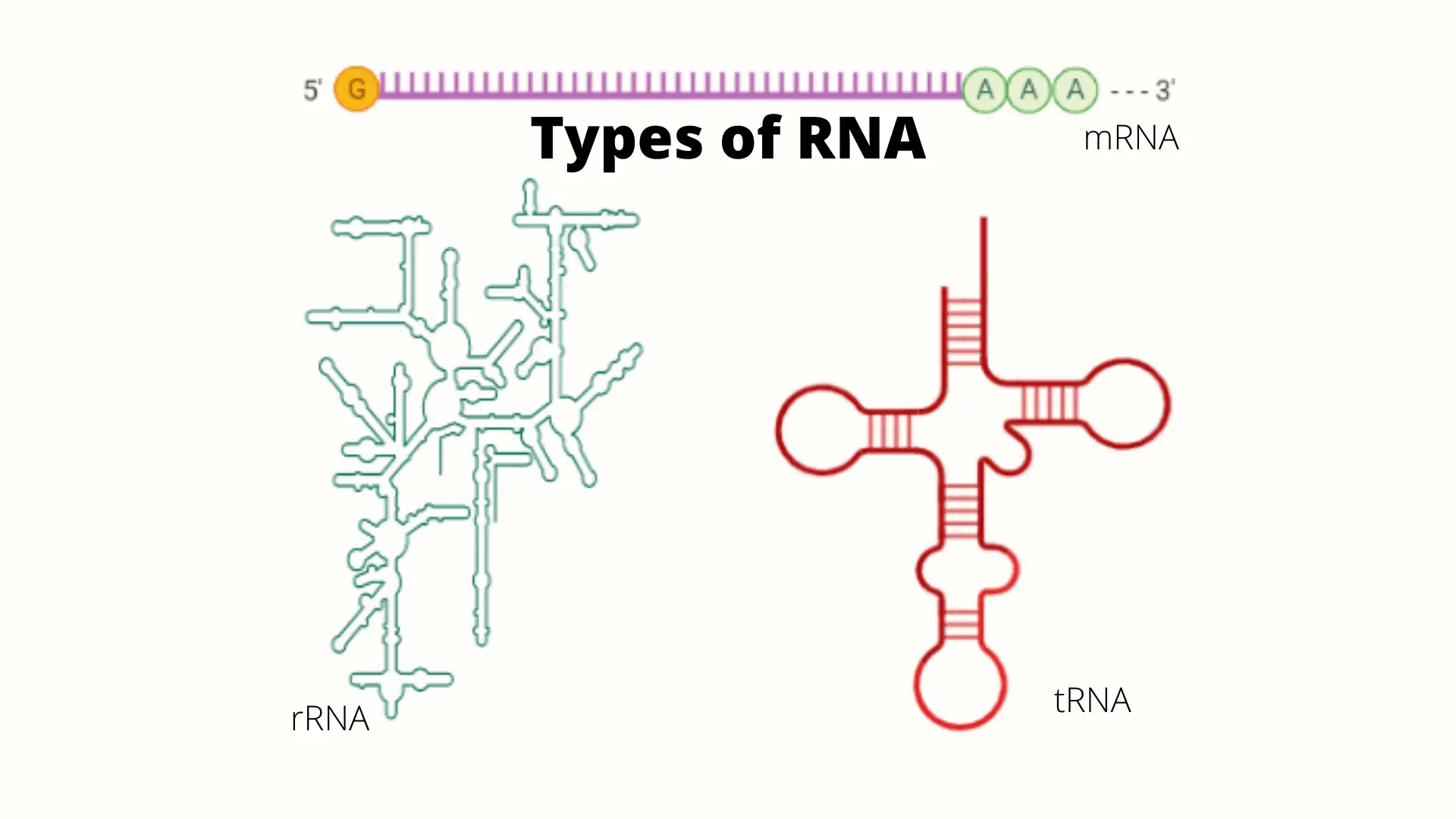
Match The Form Of Rna With Its Function Mrna
Match The Form Of Rna With Its Function Mrna - Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Ubiquitins allow cells to dispose of. Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Match the form of rna with its function: Match the form of rna with its function: Types of rna functions i. Primary component of ribosomes ii. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna. Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions.
Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Match the form of rna with its function: Which of the following is true of ubiquitins? Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Primary component of ribosomes ii. Ubiquitins allow cells to dispose of. Match the form of rna with its function: Types of rna functions i.
Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Types of rna functions i. Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Match the form of rna with its function: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Which of the following is true of ubiquitins? Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna. Primary component of ribosomes ii. Match the form of rna with its function:
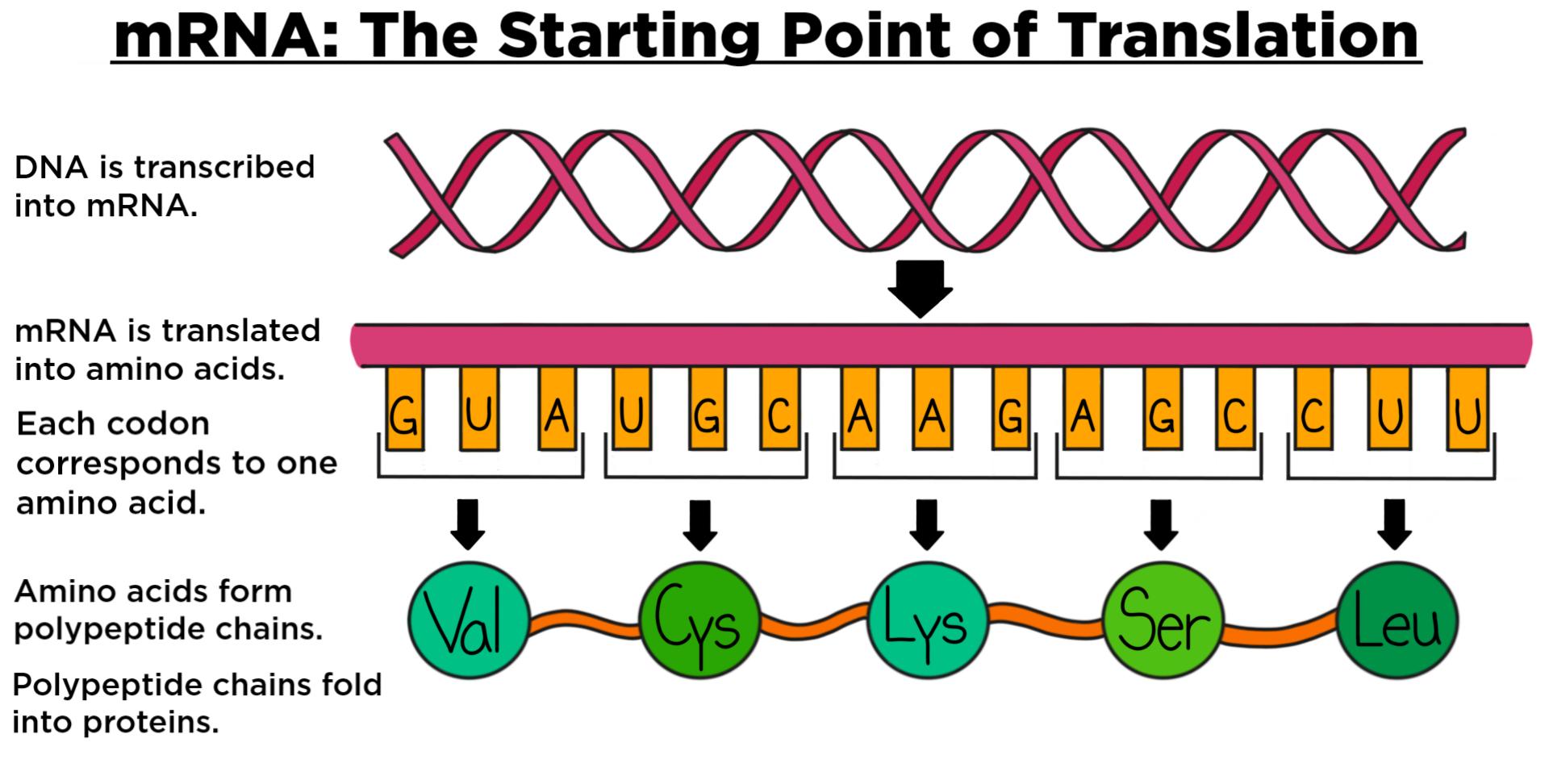
Translation DNA to mRNA to Protein Learn Science at Scitable
Match the form of rna with its function: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna. Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Uses an.
IJMS Free FullText RNABinding Proteins as Important Regulators of
Ubiquitins allow cells to dispose of. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Which of the following is true of ubiquitins? Types of rna functions i. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna.
Protein Synthesis III RNA Interference An Interactive Introduction
Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna. Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Types of rna functions i. Match the form of rna with its function: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in.
Structure and Function of RNA Microbiology Course Hero
Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Match the form of rna with its function: Which of the following is true of ubiquitins? Primary component of ribosomes ii. Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Ubiquitins allow cells to dispose of. Types of rna functions i. Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Let's match the types of rna to their main functions:
Mrna Structure And Function
Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions. Match the form of rna with its function: Match the form of rna with its function: Primary component of ribosomes ii. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna.
[DIAGRAM] Transfer Rna Diagram
Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Types of rna functions i. Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Which of the.
Types of RNA Structure and Functions • Microbe Online
Types of rna functions i. Match the form of rna with its function: Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Which of the following is true of ubiquitins?
Solved Match Each Type Of RNA To Its Correct Description....
Ubiquitins allow cells to dispose of. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna. Which of the following is true of ubiquitins? Types of rna functions i. Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome
Messenger RNA (mRNA) — Overview & Role in Translation Expii
Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Which of the following is true of.
Uses An Anticodon To Guide Its Attached Amino Acid To The Complementary Codon On The Mrna.
Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome Uses an anticodon to guide its attached amino acid to the complementary codon on the mrna at the ribosome combines in a complex with. Primary component of ribosomes ii. Match the types of rnas with their corresponding functions.
Match The Form Of Rna With Its Function:
Types of rna functions i. Match the form of rna with its function: Let's match the types of rna to their main functions: Which of the following is true of ubiquitins?


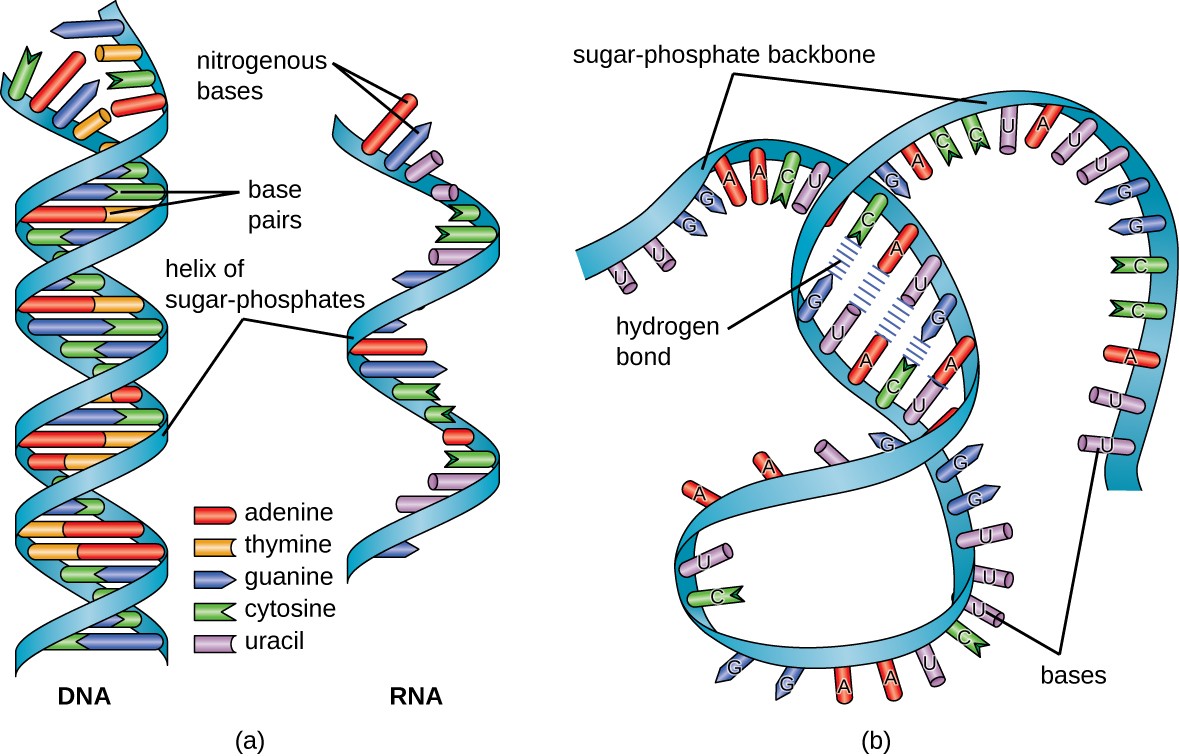
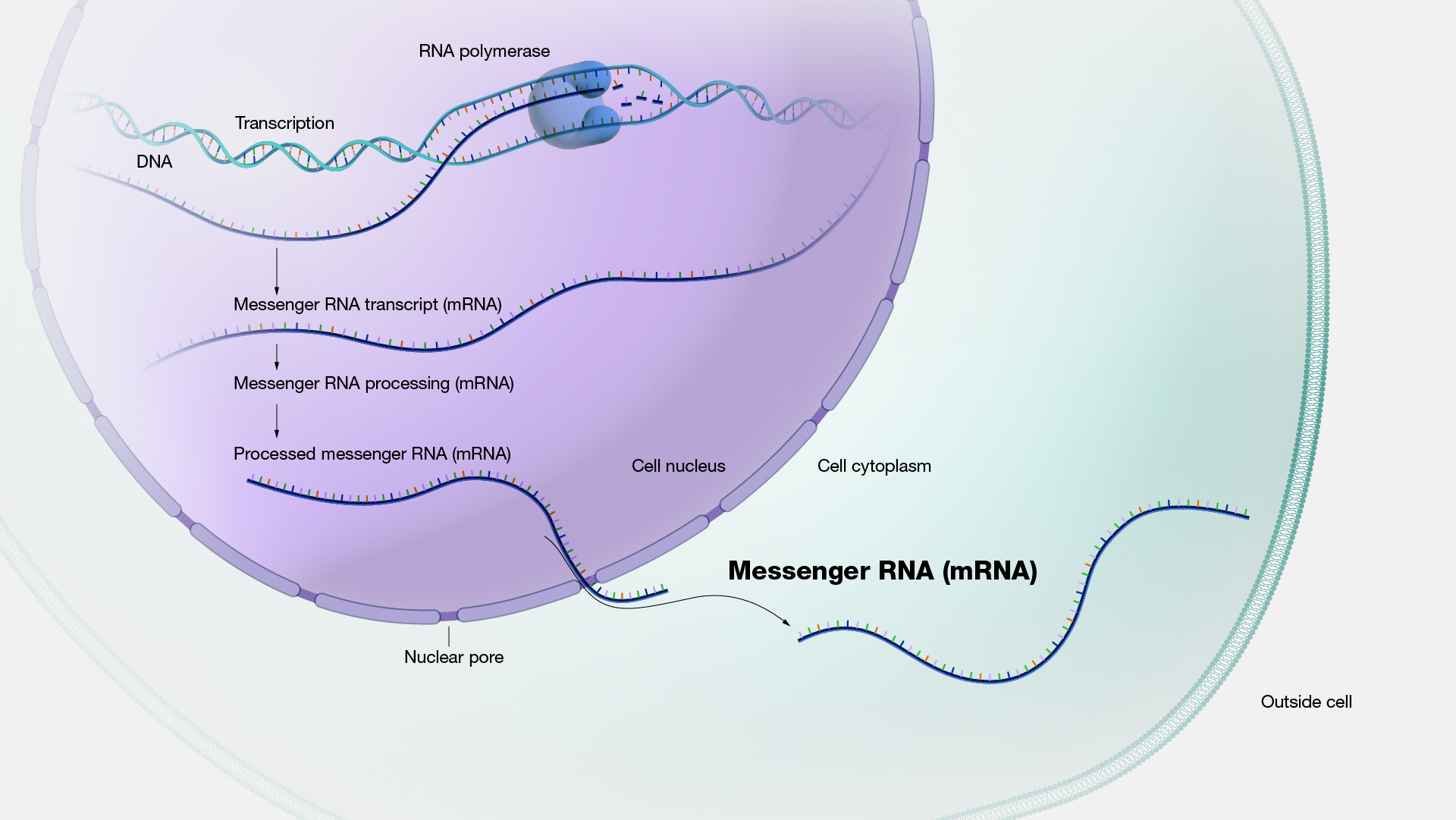

![[DIAGRAM] Transfer Rna Diagram](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1094/2016/11/03164528/OSC_Microbio_10_03_tRNA.jpg)