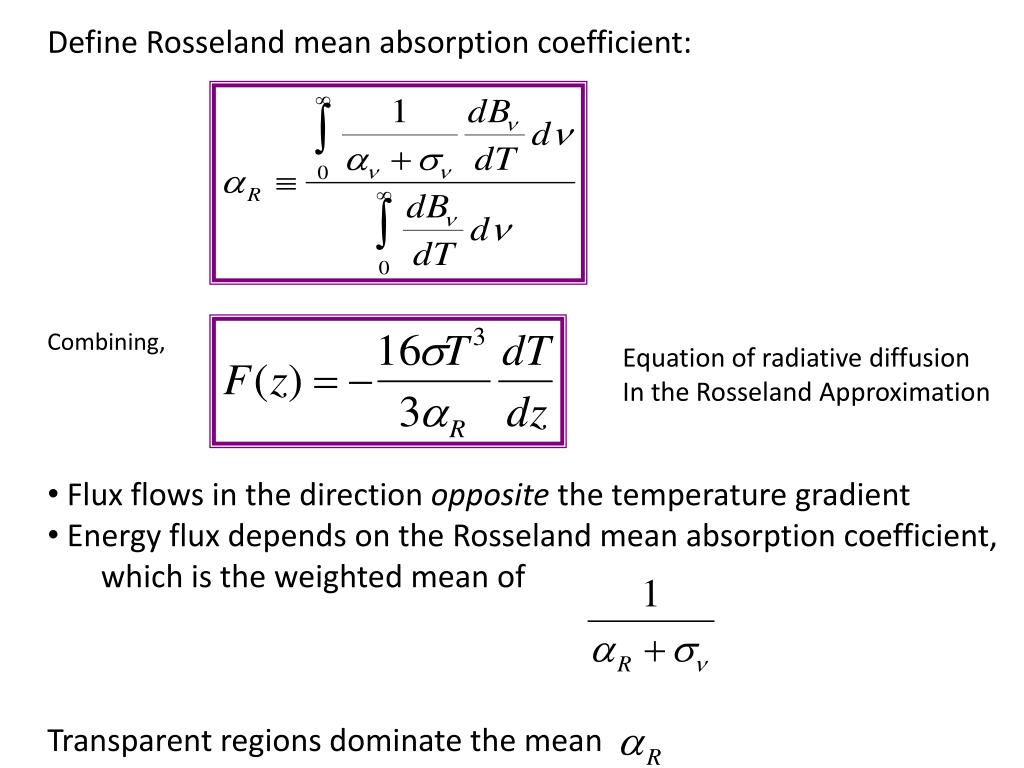
Rosseland Mean Opacity
Rosseland Mean Opacity - An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency. This mean is a strong. Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction. Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles within a star. The rosseland mean opacity (or simply rosseland mean) is a weighted average across emr frequencies of the opacity of a material, e.g., a. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =.
Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles within a star. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. The rosseland mean opacity (or simply rosseland mean) is a weighted average across emr frequencies of the opacity of a material, e.g., a. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency. The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. This mean is a strong. Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction.
In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles within a star. The rosseland mean opacity (or simply rosseland mean) is a weighted average across emr frequencies of the opacity of a material, e.g., a. Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction. This mean is a strong. The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency.
PPT Rosseland Mean Opacity PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; This mean is a strong. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency. The rosseland mean opacity (or simply rosseland.
Effective extinction opacity (top), effective albedo (middle) and
Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles within a star. The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity.
Opacity AstroBaki
The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles.
OPACITY STACK WATCH SSM
Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. In practice, and.
Rosseland Mean Opacity Astrophysics Essential, Analysis & Impact
Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. The rosseland mean opacity (or simply rosseland mean) is a weighted average across emr frequencies of the opacity of a material, e.g., a. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass.
List of available Rosseland mean opacity and opacity crosssection type
Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles within a star. The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity.
Rosseland mean opacity at seven densities as a function of
In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; The rosseland mean opacity (or.
PPT Rosseland Mean Opacity PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. This mean is a strong. In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and.
Rosseland mean opacity at three densities as a function of
The rosseland mean opacity (or simply rosseland mean) is a weighted average across emr frequencies of the opacity of a material, e.g., a. Where x is the hydrogen mass fraction. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. Playing a very important.
Effective extinction opacity (top), effective albedo (middle) and
This mean is a strong. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient; In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean.
Where X Is The Hydrogen Mass Fraction.
The rosseland mean opacity \left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{} is defined as {1\over\left\langle{\kappa}\right\rangle{}} =. In dense stellar environments, the rosseland mean opacity can significantly affect the temperature and pressure profiles within a star. In practice, and always for this course, employ averages over frequency to give rosseland mean opacities. An approximation form of the rosseland mean opacity, independent of frequency.
The Rosseland Mean Opacity (Or Simply Rosseland Mean) Is A Weighted Average Across Emr Frequencies Of The Opacity Of A Material, E.g., A.
This mean is a strong. Hence usually we employ an average opacity called the rosseland mean opacity to describe the e ective absorption. Playing a very important role in this equation is the rosseland mean opacity κ (also known as the mass absorption coefficient;