What Causes Loss Of Fatty Hilum In Lymph Node
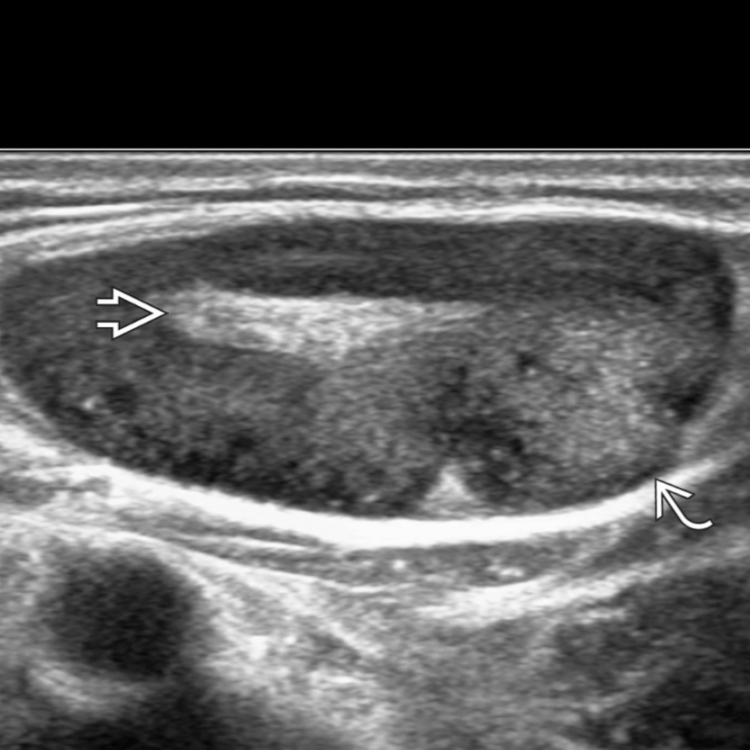
What Causes Loss Of Fatty Hilum In Lymph Node - Suspicious ultrasound features of lymph nodes were the following: And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? Predominantly hypoechoic although metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma tend to be hyperechoic due to the intranodal deposition of. This loss may suggest several conditions, including:.
Predominantly hypoechoic although metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma tend to be hyperechoic due to the intranodal deposition of. The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. Suspicious ultrasound features of lymph nodes were the following: Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? This loss may suggest several conditions, including:. The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),.
Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? Predominantly hypoechoic although metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma tend to be hyperechoic due to the intranodal deposition of. This loss may suggest several conditions, including:. The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. Suspicious ultrasound features of lymph nodes were the following: Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),.
Structure Of Lymph Node Diagram
This loss may suggest several conditions, including:. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? Suspicious ultrasound features of lymph nodes were the following:
Lymph Node Evaluation in Breast Imaging Clinical Tree
This loss may suggest several conditions, including:. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an.
Lymph Node Abnormality Radiology Key
The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty.
Hilum Chest X Ray
This loss may suggest several conditions, including:. Predominantly hypoechoic although metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma tend to be hyperechoic due to the intranodal deposition of. I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. Loss of fatty hilum,.
Normal elliptical node with echogenic hilum. Download Scientific Diagram
The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans,.
Involved lymph node round shape, loss of fatty hilum, and hypoechoic
The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? I.
Involved lymph node round shape, loss of fatty hilum, and hypoechoic
The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? Predominantly hypoechoic although metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma tend to be hyperechoic due to.
Ultrasound of an axillary lymph node with absence of fat hilum, round
Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. This loss may suggest several conditions, including:.
Lymph Node Ultrasound Significance of Short Axis, Fatty Hilum
I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging. Predominantly hypoechoic although metastatic lymph nodes from papillary thyroid carcinoma tend to be hyperechoic due to the intranodal deposition of. The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is.
Lymph Node Histology Slide
And what causes a lymph node to become anechoic? Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right? The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph.
Predominantly Hypoechoic Although Metastatic Lymph Nodes From Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Tend To Be Hyperechoic Due To The Intranodal Deposition Of.
The presence of a fatty hilum in a lymph node is a normal feature of lymph nodes. Suspicious ultrasound features of lymph nodes were the following: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, ct scans, and mri are essential tools in evaluating these. I mean if this is a lymph node, it is troubled, right?
And What Causes A Lymph Node To Become Anechoic?
Do you know why a lymph node no longer has a fatty hilum? Loss of fatty hilum, cystic change, calcification, hyperechogenicity (higher echogenicity than the surrounding muscles),. This loss may suggest several conditions, including:. The loss of the fatty hilum in a lymph node is an important finding in medical imaging.







:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5794/7oN25FG47g7JVVLnQhVg7g_Hilum_of_the_lymph_node.png.jpeg)