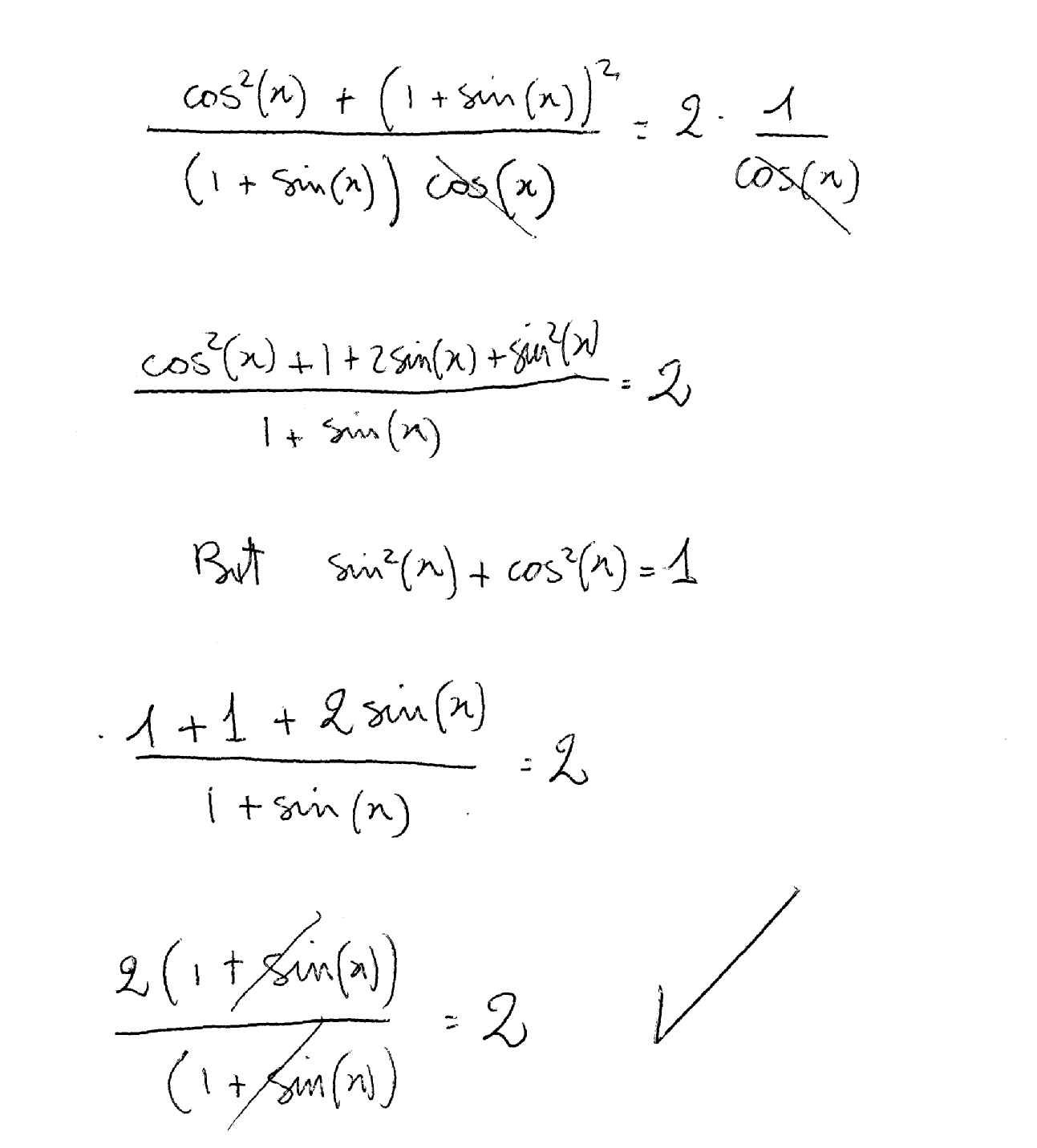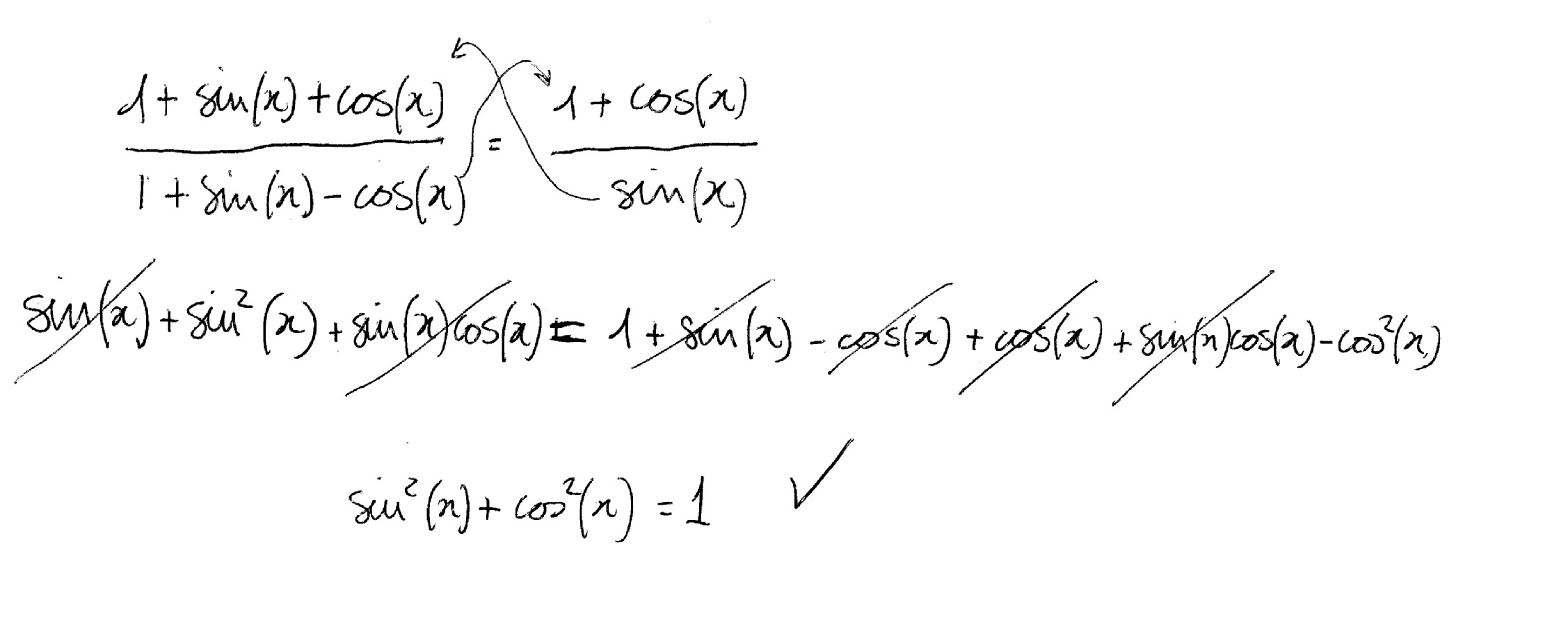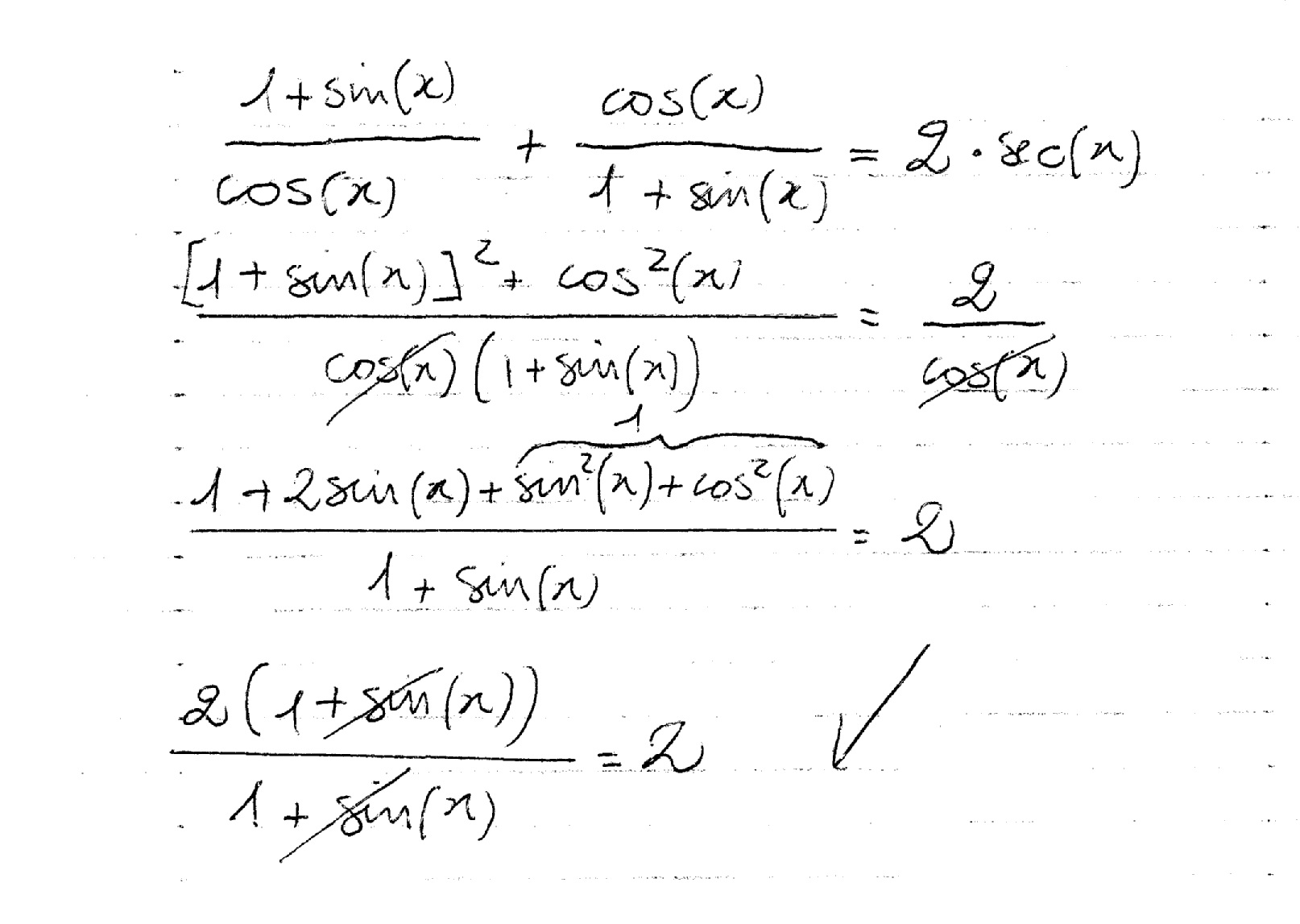What Is 1 Sinx
What Is 1 Sinx - The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. What is sin 3x formula? All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows:
The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: What is sin 3x formula? Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. All trigonometric formulas are divided into two.
Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: What is sin 3x formula? The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined.
Trigonometric Identity (1 Cosx)/sinx Sinx/(1 Cosx) 2/sinx, 43 OFF
The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: What is sin 3x formula? The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined.
How do you verify this identity (cosx)/(1+sinx) + (1+sinx)/(cosx
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. What is sin 3x formula?
How do you prove (1 + sinx + cosx)/(1 + sinx cosx) = (1 + cosx)/sinx
Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. The 1 plus sinx idenity.
What Is 1/sinx Equal To
What is sin 3x formula? The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the.
integrate 1 sinx dx/sinx(1+sinx)
The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. What is sin 3x formula?
continuity Proof that (1/sinx)(1/x) is continuous Mathematics
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. What is sin 3x formula? Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given.
SOLUTION Integrate ?(1sinx+cosx)/(1cosx+sinx) dx Studypool
Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of.
1sinx
The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of.
What Is 1/sinx Equal To
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. What is sin 3x formula? Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas.
What Is 1/sinx Equal To
All trigonometric formulas are divided into two. What is sin 3x formula? The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. The trigonometric identities are based on all the six.
All Trigonometric Formulas Are Divided Into Two.
The trigonometric identities are based on all the six. In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. The 1 plus sinx idenity is given as follows: Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions.