What Is Covalent Catalysis
What Is Covalent Catalysis - Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and at least one of the substrates involved in the reaction. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. A typical way is to add a. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will use to catalyze a specific reaction, which involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between a substrate. Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become. One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to change the reaction mechanism in ways which introduces new steps with lower activation energy. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to.
Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will use to catalyze a specific reaction, which involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between a substrate. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to change the reaction mechanism in ways which introduces new steps with lower activation energy. A typical way is to add a. Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and at least one of the substrates involved in the reaction. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction.
One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to change the reaction mechanism in ways which introduces new steps with lower activation energy. Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. A typical way is to add a. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will use to catalyze a specific reaction, which involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between a substrate. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and at least one of the substrates involved in the reaction.
SOLVED 1. What is covalent catalysis? Describe the two parts of a
Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will use to catalyze a specific reaction, which involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between a substrate. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate.
Catalysis Fundamentals Chemical Engineering Page 1
Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will use to catalyze a specific reaction, which involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between a substrate. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. A typical way is to add a. One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to change the reaction mechanism in.
[ANSWERED] Label the catalytic strategies below as covalent catalysis
Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and at least one of the substrates involved in the reaction. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. Covalent catalysis occurs when.
Electrostatic catalysis applied to covalent inhibition. a, Common
One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to change the reaction mechanism in ways which introduces new steps with lower activation energy. A typical way is to add a. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that.
Catalysis
Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a.
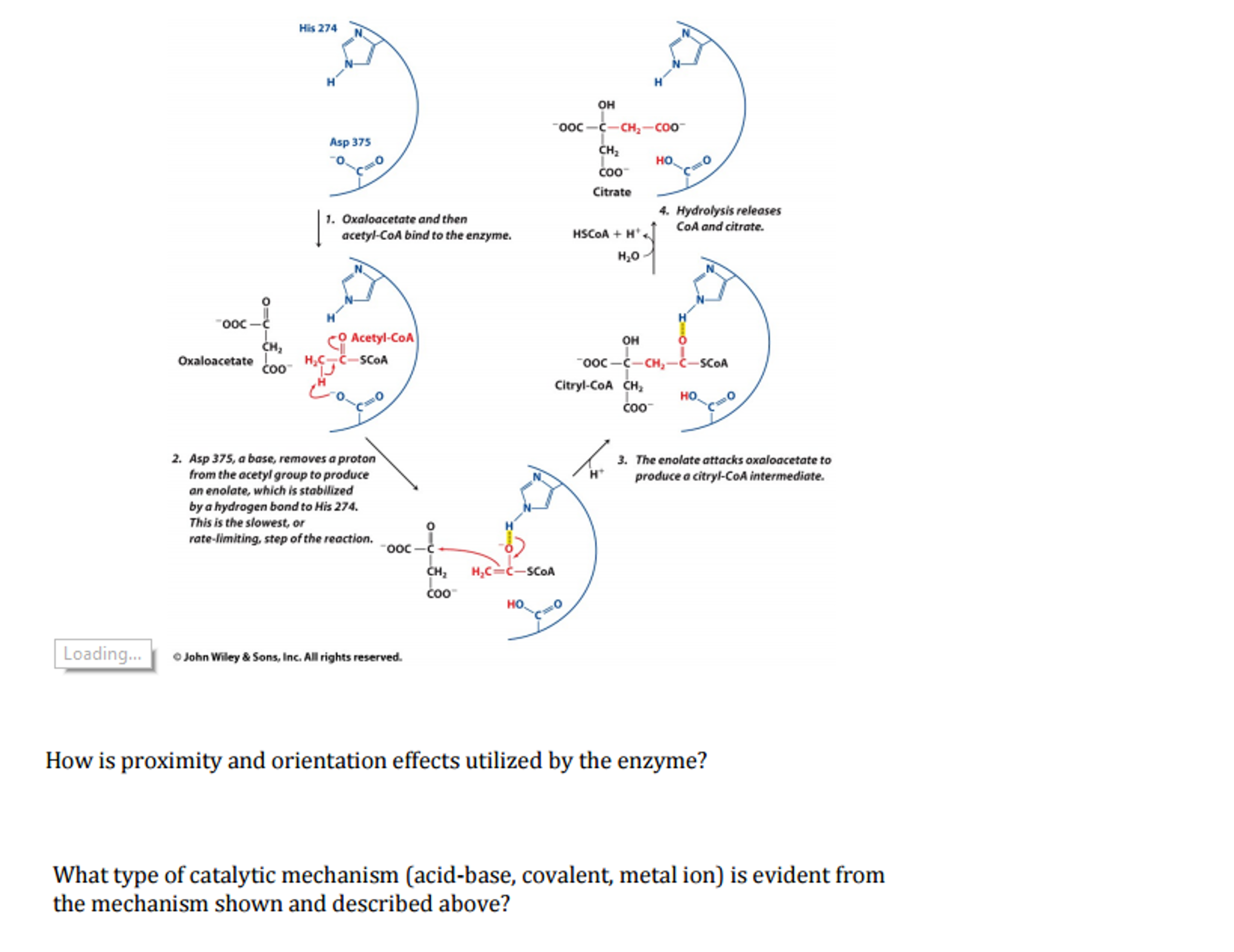
how does the proximity and orientation effect occur
Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. A typical way is to add a. Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an.
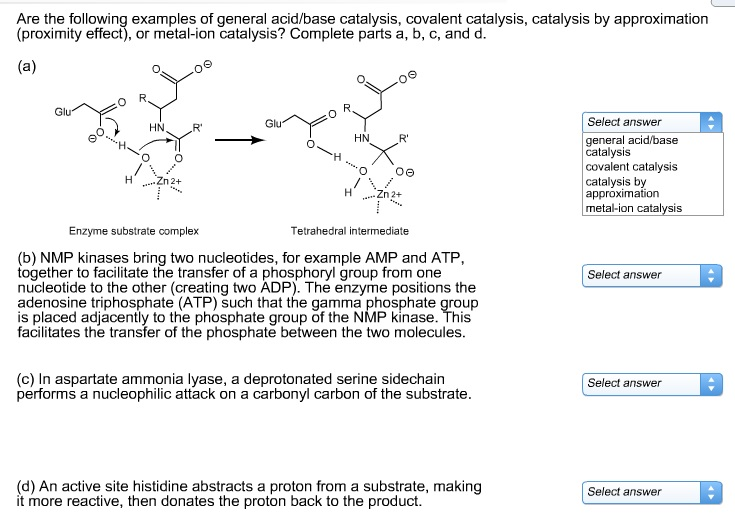
Are the following examples of general acid/base
Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will use to catalyze a specific reaction, which involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between a substrate. One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to.
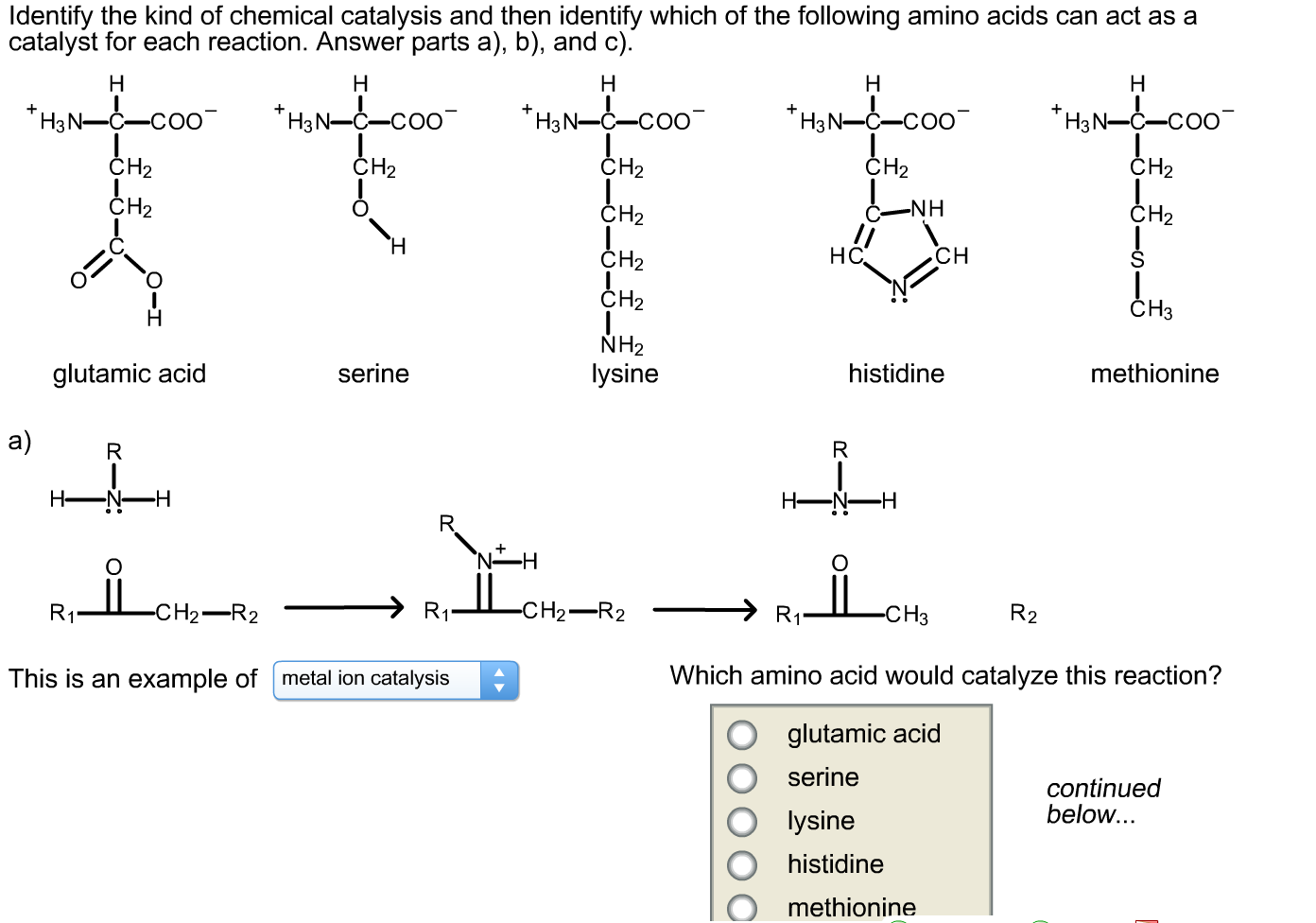
Solved Please help!!! Which of the following is acid base
Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and at least one of the substrates involved in the.
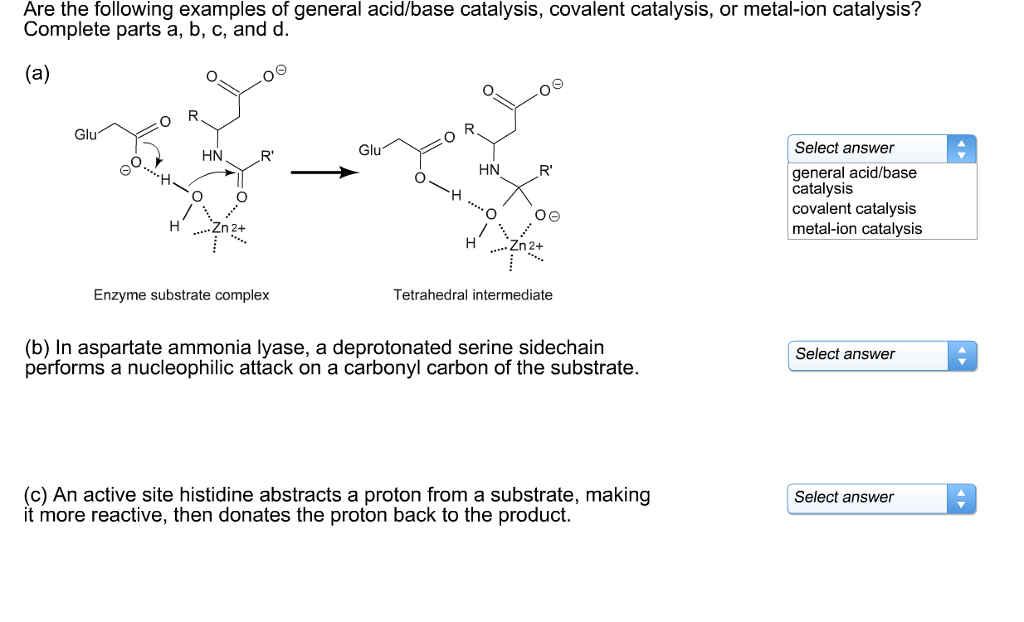
Solved Are the following examples of general acid/base
One way to change the activation energy of the reaction is to change the reaction mechanism in ways which introduces new steps with lower activation energy. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. A typical way is to add a. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Covalent catalysis is.
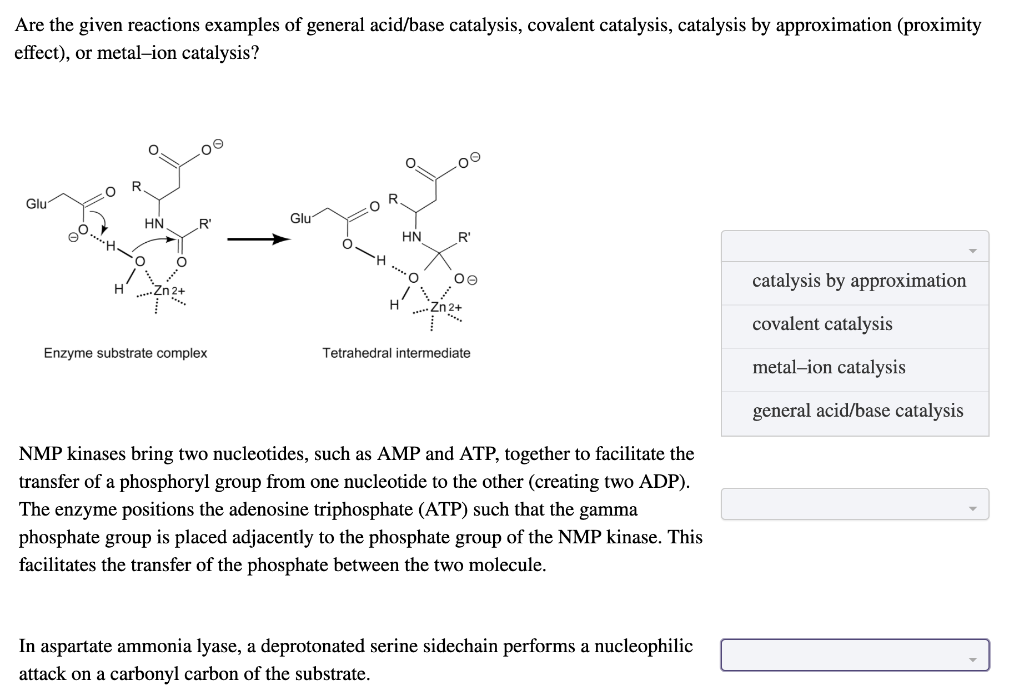
Solved Are the given reactions examples of general acid/base
Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. A typical way is to add a. Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent.
Covalent Catalysis Is One Of The Four Strategies That An Enzyme Will Use To Catalyze A Specific Reaction, Which Involves The Formation Of A Transient Covalent Bond Between A Substrate.
Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between an enzyme and a substrate, creating an intermediate molecule that accelerates the reaction rate compared to. Often times this involves nucleophilic catalysis. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent bond between the enzyme and at least one of the substrates involved in the reaction. A typical way is to add a.
One Way To Change The Activation Energy Of The Reaction Is To Change The Reaction Mechanism In Ways Which Introduces New Steps With Lower Activation Energy.
Covalent catalysis is one of the four strategies that an enzyme will employ to catalyze a specific reaction. Covalent catalysis occurs when the substrate(s) in an enzymatic reaction become.

![[ANSWERED] Label the catalytic strategies below as covalent catalysis](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20230225013819557164-4123275.jpg?h=512)