What Process Permits Absorption Of Glucose Into Cells
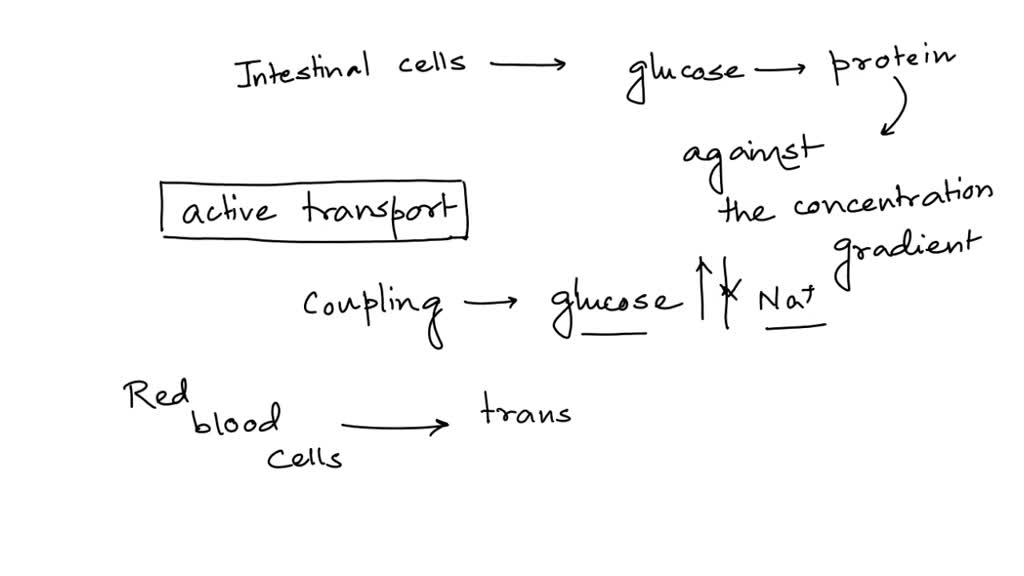
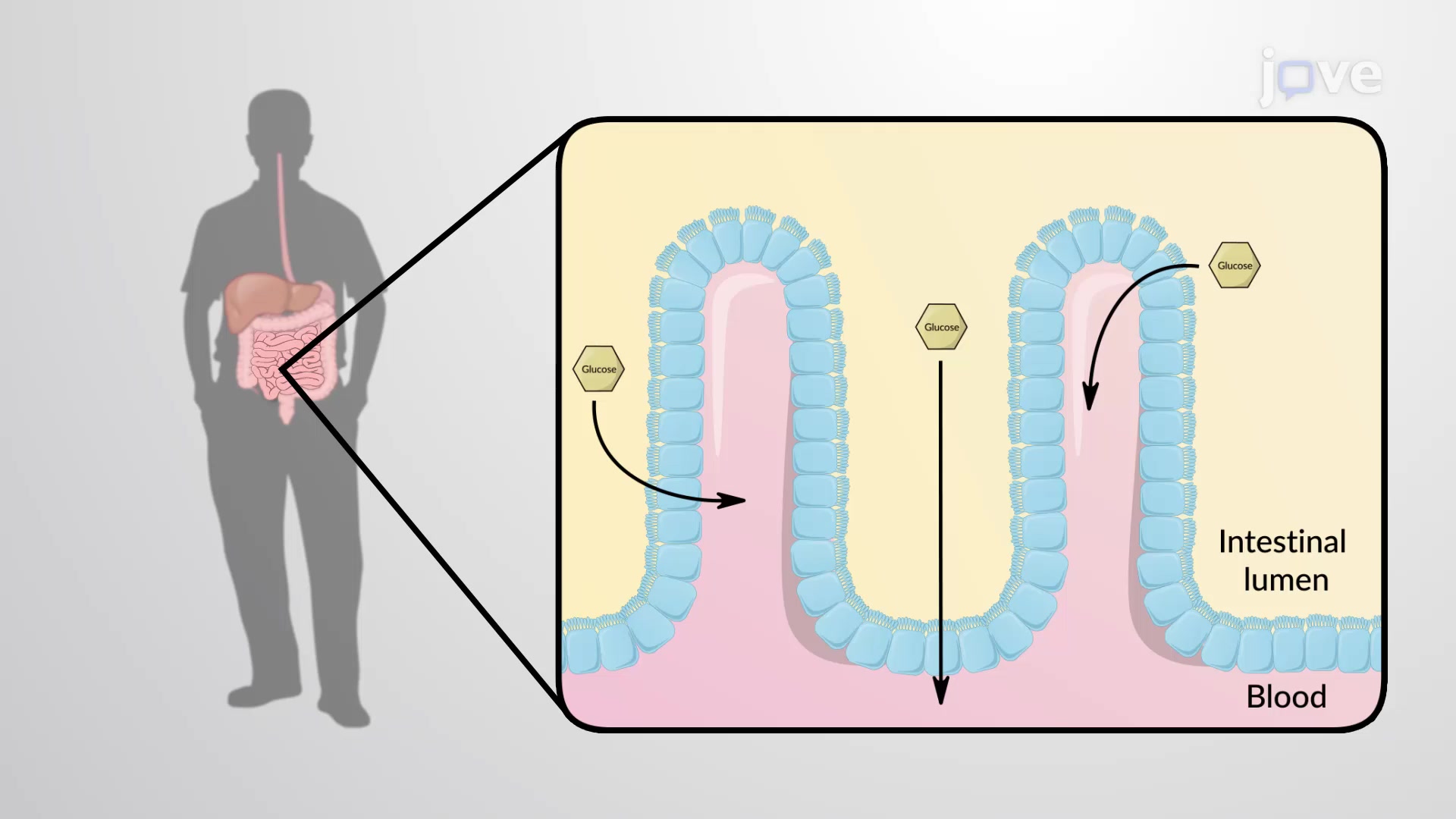
What Process Permits Absorption Of Glucose Into Cells - It is formed during tissue repair. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What is the significance of granulation tissue? What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? In more detail, the absorption of. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources.
Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. In more detail, the absorption of. What is the significance of granulation tissue? What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? It is formed during tissue repair.
Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. It is formed during tissue repair. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. What is the significance of granulation tissue? In more detail, the absorption of. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells?
Diagram showing the process of glucose absorption in cells with and
What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. What is the significance of granulation tissue? Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. In more detail, the absorption of.
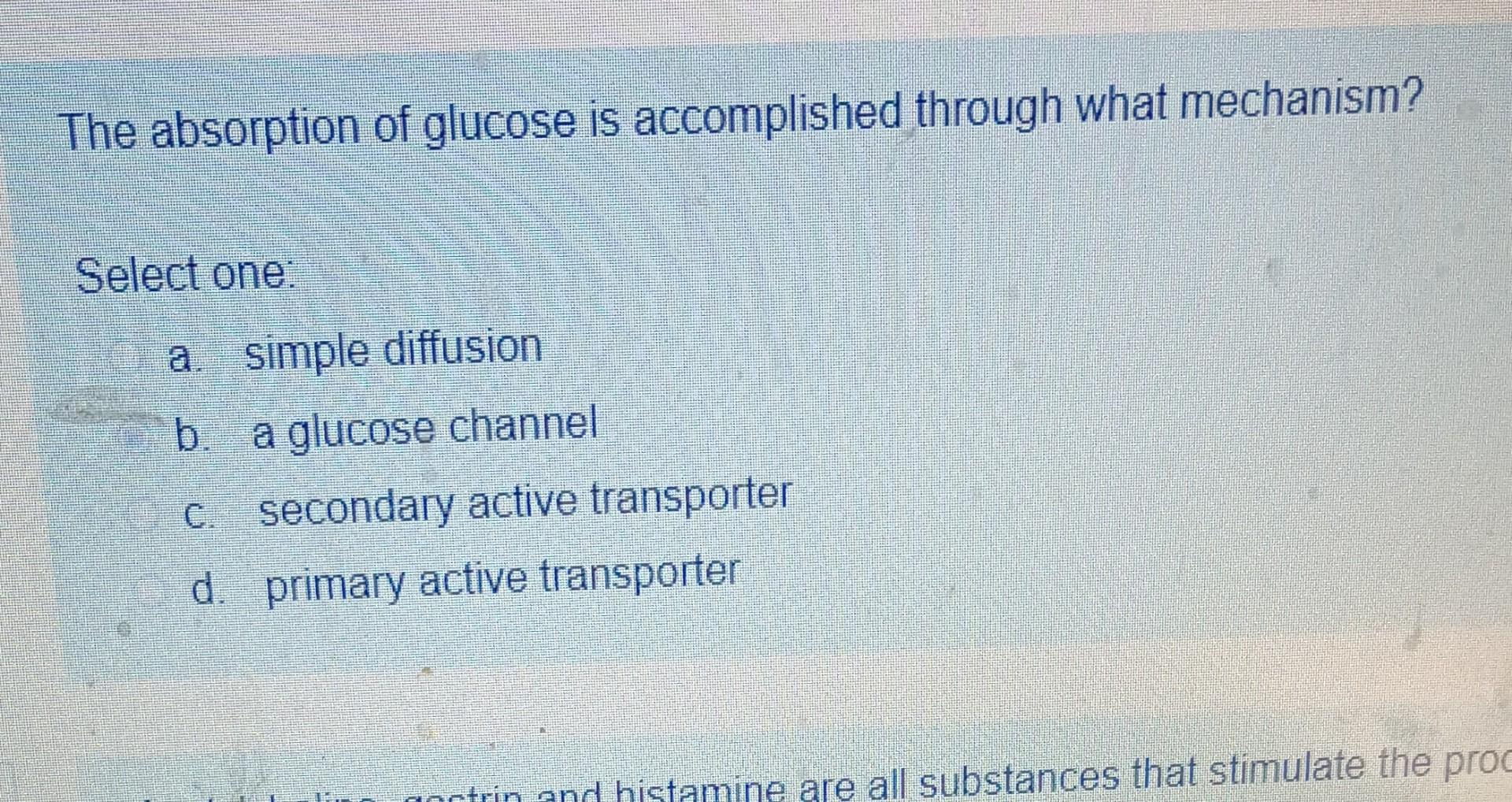
Solved The absorption of glucose is through
What is the significance of granulation tissue? What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. It is formed during tissue repair.
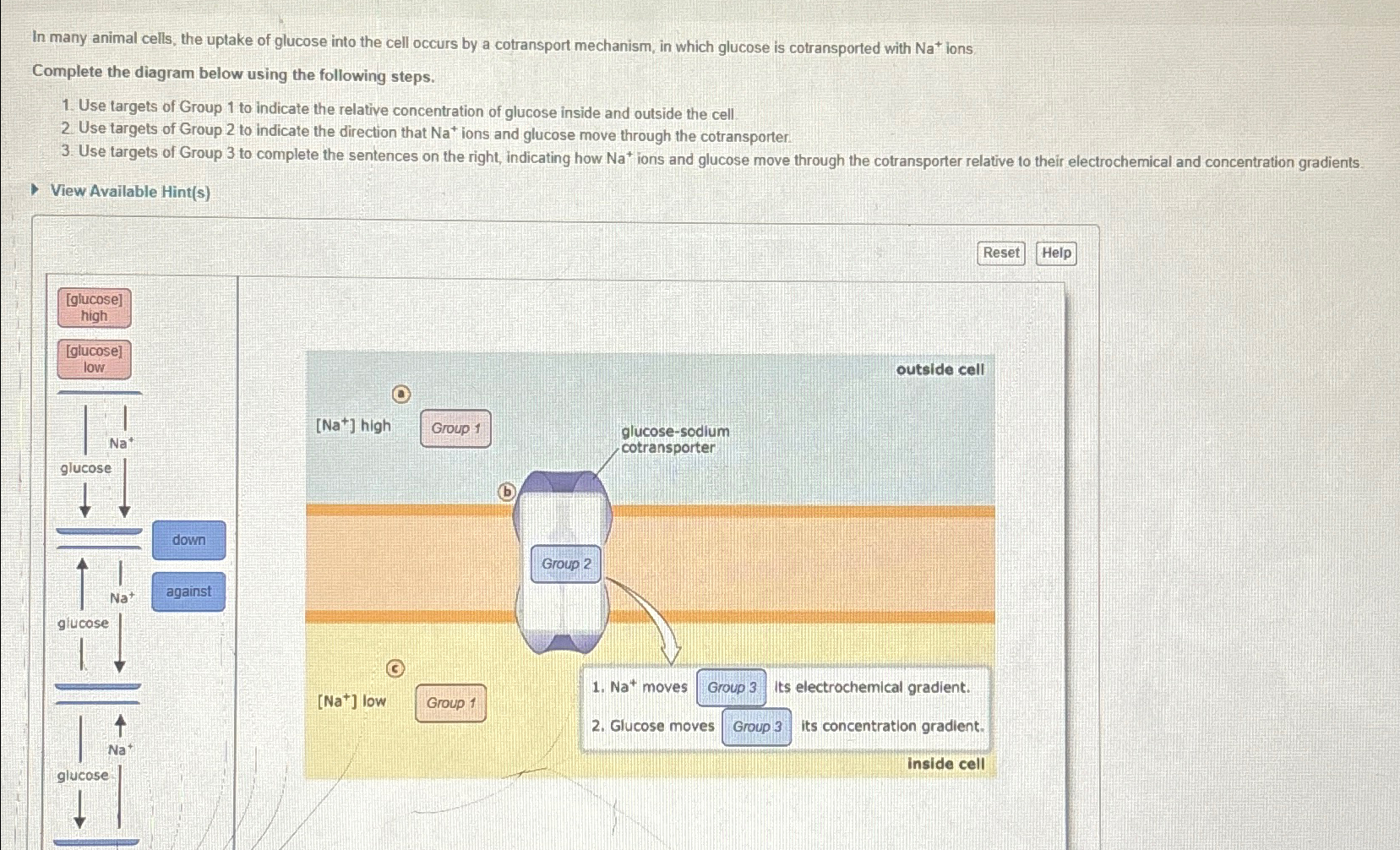
Solved In many animal cells, the uptake of glucose into the
In more detail, the absorption of. It is formed during tissue repair. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. What is the significance of granulation tissue? What process permits absorption of glucose into cells?
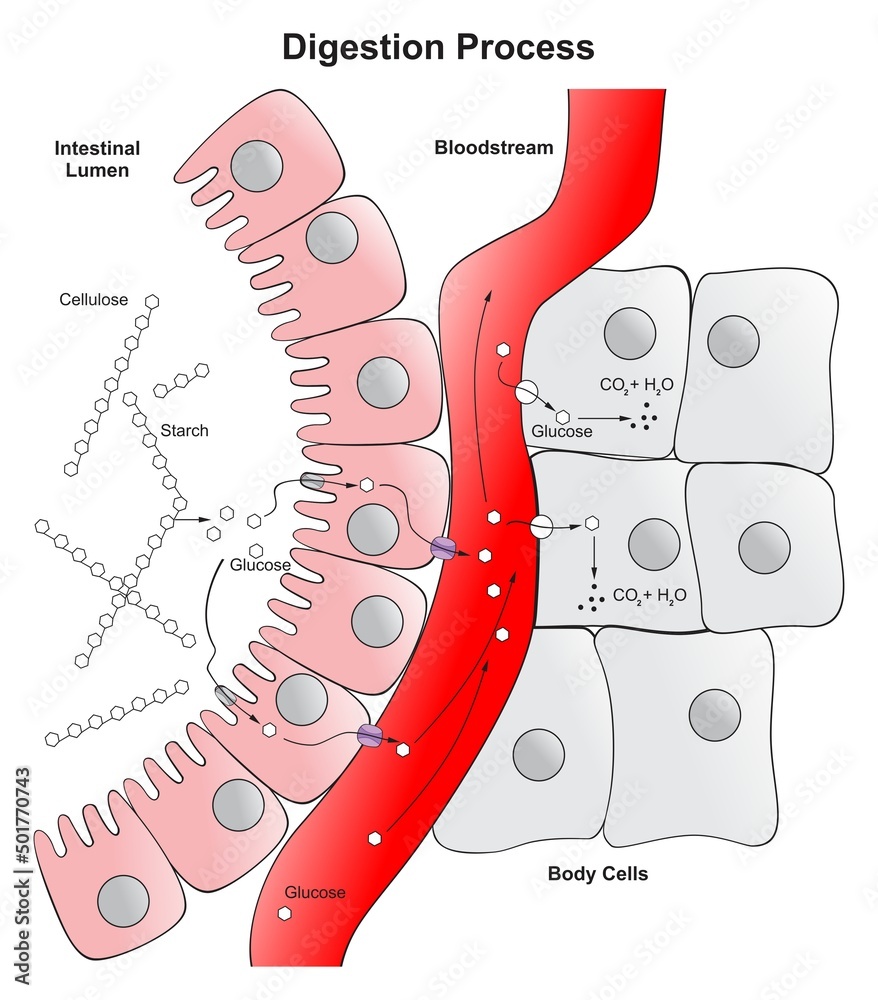
Digestion process in human body infographic diagram cellulose glucose
In more detail, the absorption of. What is the significance of granulation tissue? What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the.
Insulin Is The Key That Unlocks The Cells Glucose Channel Vector
In more detail, the absorption of. Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. What is the significance of granulation tissue? What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the.
SOLVED Glucose provides energy for cells. Different cells have
Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What process permits absorption.
Cotransport and Glucose Absorption Diagram Quizlet
In more detail, the absorption of. Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. It is formed during tissue repair. Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport.
Glucose Absorption Into the Small Intestine Cell Biology JoVe
What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What is the significance of granulation tissue? In more detail, the absorption of. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport.
Absorption of glucose by the cell type 1 Vector Image
What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What is the significance of granulation tissue? It is formed during tissue repair. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? In more detail, the absorption of.
Absorption of glucose by the cell diabetes Vector Image
What is the significance of granulation tissue? Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. What transport process can create a concentration gradient for sodium across the. In more detail, the absorption of. Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary.
What Transport Process Can Create A Concentration Gradient For Sodium Across The.
Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine via a process called active transport. What process permits absorption of glucose into cells? What is the significance of granulation tissue? In more detail, the absorption of.
What Process Permits Absorption Of Glucose Into Cells?
Sglts are present on the luminal surfaces of cells lining the small intestine where they absorb glucose from dietary sources. It is formed during tissue repair.